Java OIO¶
Java OIO 就是 Java Old IO,也就是 java.io 包下定义的哪些类的 IO,是阻塞同步 IO。
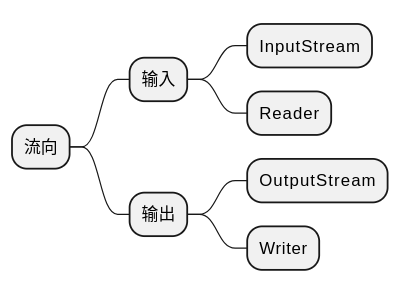
按流向分类¶
这里的流向是站在 CPU 的角度进行设计的:
按传输方式分类¶
按数据操作分类¶
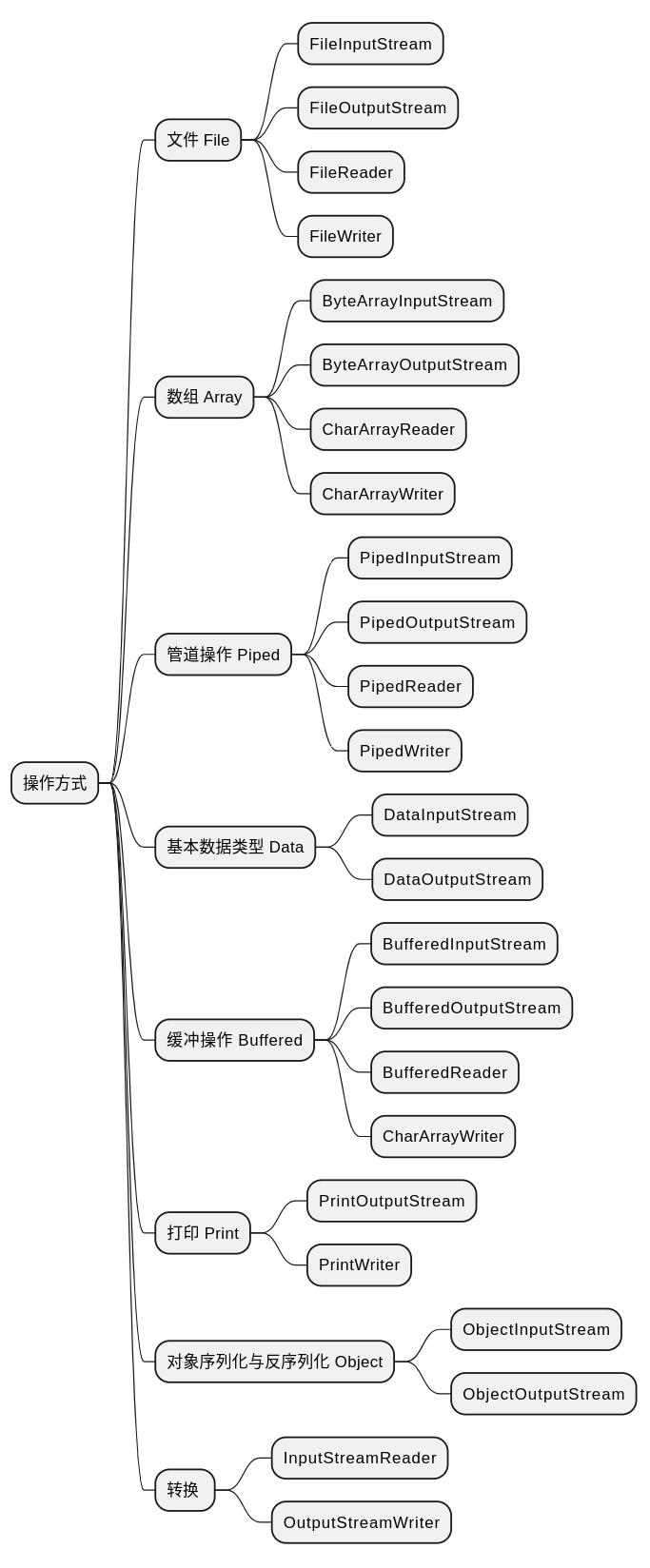
文件 File¶
FileInputStream
FileOutputStream
FileReader
FileWriter
FileInputStream 内部又一个文件描述符,读写本质上都调用 native 方法进行文件读写(经过JVM进行文件读写的系统调用),FileOutputStream 类似。
FileReader 本质上是使用装饰器模式,装饰一个FileInputStream,FileWriter 类似。
// FileInputStream 构造方法
public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {
String name = (file != null ? file.getPath() : null);
fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.attach(this);
path = name;
open(name);
FileCleanable.register(fd); // open set the fd, register the cleanup
}
// FileReader 构造方法
public FileReader(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {
super(new FileInputStream(fileName));
}
数组 Array¶
ByteArrayInputStream
ByteArrayOutputStream
CharArrayReader
CharArrayWriter
本质上都是内部定义了一个数组,读写都是对内部数组进行读写。
protected byte[] buf;
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf, int offset, int length) {
this.buf = buf;
this.pos = offset;
this.count = Math.min(offset + length, buf.length);
this.mark = offset;
}
protected char[] buf;
public CharArrayReader(char[] buf) {
this.buf = buf;
this.pos = 0;
this.count = buf.length;
}
管道操作 Piped¶
PipedInputStream
PipedOutputStream
PipedReader
PipedWriter 这里的管道是进行线程间通信的。一个线程使用 writer 写数据,另外一个线程使用 reader 读取数据。
PipedWriter writer = new PipedWriter();
PipedReader reader = new PipedReader(writer);
基本数据类型 Data¶
DataInputStream
DataOutputStream
DataInputStream 本质上是使用装饰器模式,装饰一个 InputStream,然后提供 Java 基本数据类型的读取,DataOutputStream 类似。
boolean readBoolean() throws IOException;
byte readByte() throws IOException;
int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException;
short readShort() throws IOException;
int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException;
char readChar() throws IOException;
int readInt() throws IOException;
long readLong() throws IOException;
float readFloat() throws IOException;
double readDouble() throws IOException;
String readLine() throws IOException;
缓冲操作 Buffered¶
BufferedInputStream
BufferedOutputStream
BufferedReader
BufferedWriter
BufferedInputStream 使用装饰器模式,装饰一个 InputStream,内部维护一个缓存数组( volatile byte[] buf),进行批量读写,避免频繁系统调用,提高性能,其他类似。
public int read() throws IOException {
if (lock != null) {
lock.lock();
try {
return implRead();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
synchronized (this) {
return implRead();
}
}
}
private int implRead() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
打印 Print¶
PrintOutputStream
PrintWriter
本质上都是使用装饰器模式,装饰一个其他的 Writer,然后提供了基本类型的输出。
print(char)
print(int)
print(float)
print(double)
print(long)
print(short)
print(Object)
对象序列化与反序列化 Object¶
ObjectInputStream
ObjectOutputStream
也是使用装饰器模式,装饰一个其他的流,然后提供了基本类型和Object的操作。
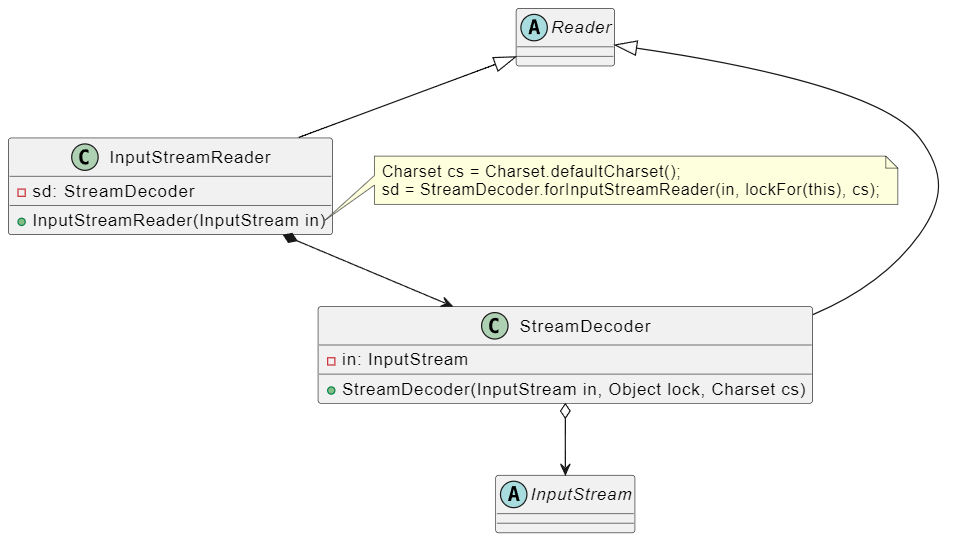
转换¶
InputStreamReader
OutputStreamWriter
InputStreamReader 继承了 Reader,使用装饰器模式,装饰一个 InputStream ,从而可以使原来的字节流具备字符操作的能力。OutputStreamWriter 同理。