Java 四种引用¶
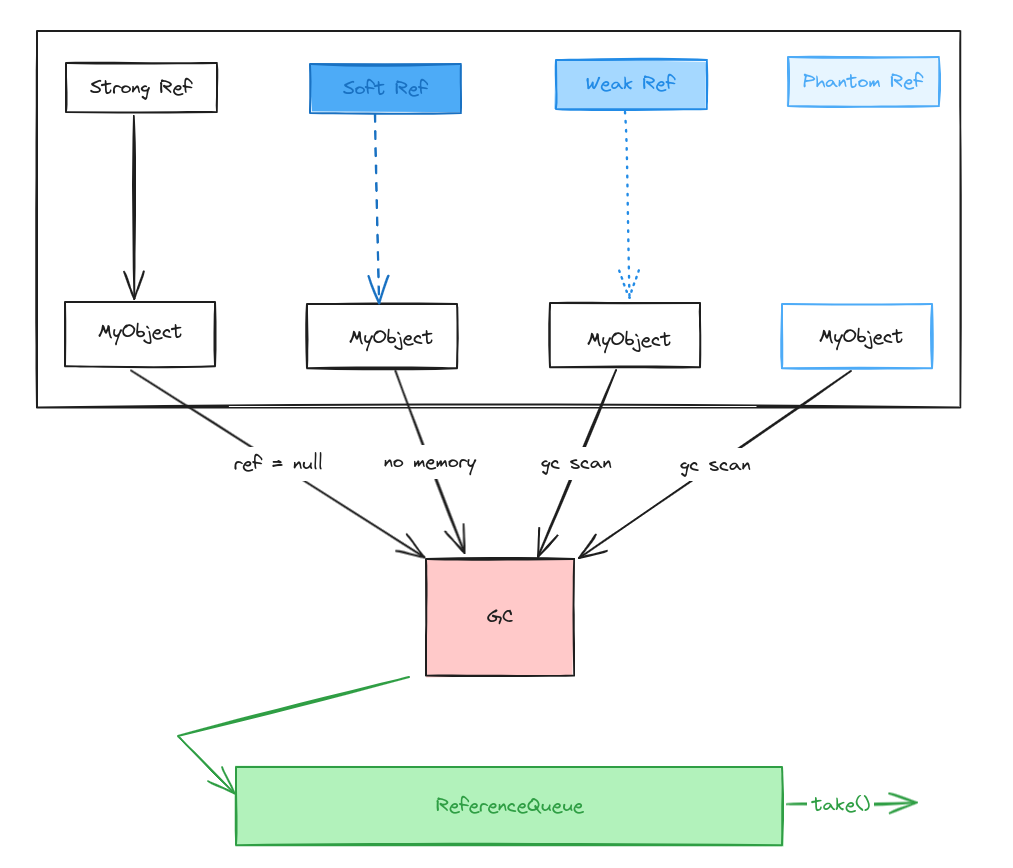
1. 强引用 Strong¶
声明¶
最常见的引用类型,没有特别标记的引用都是强引用。
String strongRef1 = new Sting();
String strongRef2 = "123";
特性¶
垃圾收集器绝不会回收它。当内存空间不足时,Java 宁愿抛出 OutOfMemoryError 也不会回收这些对象。
如果要让垃圾回收器尽早的回收它,可以显式的将 null 赋给它,比如 `ArrayList.remove()。
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
使用场景¶
普通对象的创建,一般引用开发中,大部分情况下都是使用强引用。
2. 软引用 Soft¶
声明¶
使用 SoftReference 定义的引用,可选择性指定ReferenceQueue。
SoftReference<String> softReference = new SoftReference<>(new Object());
特性¶
如果一个对象只有弱引用,被 GC 扫描到时,内存空间不足,才将其视为垃圾进行回收。
使用场景¶
描述一些还有用但并非必需的对象,如内存敏感的缓存
小心
并不建议直接使用软引用或弱引用实现缓存,因为:
增加了复杂度和维护成本。需要额外考虑对象的生命周期和引用使用方式。
可能影响缓存性能。由于软引用和弱引用的特性,垃圾回收器需要更频繁地扫描内存,以查找可以回收的对象。
会导致缓存的不确定性。由于软引用和弱引用的特性,缓存值可能会被过早回收,导致缓存失效。
3. 弱引用 Weak¶
声明¶
使用 WeakReference 定义的引用,可选择性指定ReferenceQueue。
WeakReference<String> weakReference = new WeakReference<>(new Object());
特性¶
如果一个对象只有弱引用,被 GC 扫描到就回收(不管当前内存空间足够与否)。
真正回收前会先执行下对象的
finalize()方法,所以有一次复活的机会。对象被垃圾回收时,会先将其放入
ReferenceQueue
使用场景¶
容易内存泄漏的地方。
WeakHashMap Entry 的 key
ThreadLocalMap Entry 的 key(ThreadLocal)
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
4. 虚引用 Phantom¶
声明¶
使用 PhantomReference 定义的引用,而且必须指定ReferenceQueue。
ReferenceQueue<String> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
PhantomReference<String> phantomReference = new PhantomReference<>(new Object(), queue);
特性¶
如果一个对象只有虚引用,被 GC 扫描到就回收。
当垃圾收集器决定回收对象时,虚引用会被添加到与之关联的引用队列中。
它不能单独使用,必须和引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用。虚引用主要用于跟踪对象被垃圾回收的活动。
使用场景¶
PhantomReference 的主要作用是在对象被垃圾回收前,执行一些清理操作。例如,在使用 DirectByteBuffer 时,需要手动释放 ByteBuffer 占用的内存。可以使用 PhantomReference 来跟踪 DirectByteBuffer 对象是否已经没有任何强引用,只有虚引用时,就被加入到 ReferenceQueue,则可以使用一个专门的清理线程,消费 ReferenceQueue 中的元素,在消费方法中释放 ByteBuffer 占用的内存。
import java.lang.ref.PhantomReference;
import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class DirectByteBufferCleaner extends PhantomReference<ByteBuffer> implements Runnable {
private static final ReferenceQueue<ByteBuffer> QUEUE = new ReferenceQueue<>();
private long address;
public DirectByteBufferCleaner(ByteBuffer buffer, long address) {
super(buffer, QUEUE);
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 释放ByteBuffer占用的内存
unsafe.freeMemory(address);
}
// 启动清理线程
public static void startCleanerThread() {
Thread cleanerThread = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
DirectByteBufferCleaner cleaner = (DirectByteBufferCleaner) QUEUE.remove();
cleaner.run();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// ignore
}
}
});
cleanerThread.setDaemon(true);
cleanerThread.start();
}
}
代码示例¶
/**
* strongRef: reference=hello, pollResult=Optional.empty
* before gc: reference=hello, pollResult=Optional.empty
* [0.524s][info][gc] GC(1) Pause Full (System.gc()) 9M->4M(40M) 8.716ms
* after gc: reference=hello, pollResult=Optional.empty
*/
@Test
public void softReference() throws InterruptedException {
MyObject hello = new MyObject("hello");
ReferenceQueue<MyObject> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
SoftReference<MyObject> reference = new SoftReference<>(hello, queue);
System.out.printf("strongRef: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
hello = null;
System.out.printf("before gc: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
System.gc();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.printf("after gc: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
}
/**
* strongRef: reference=hello, pollResult=Optional.empty
* before gc: reference=hello, pollResult=Optional.empty
* [0.524s][info][gc] GC(1) Pause Full (System.gc()) 9M->4M(40M) 7.889ms
* after gc: reference=null, pollResult=Optional[java.lang.ref.WeakReference@4450d156]
*/
@Test
public void weakReference() throws InterruptedException {
MyObject hello = new MyObject("hello");
ReferenceQueue<MyObject> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
WeakReference<MyObject> reference = new WeakReference<>(hello, queue);
System.out.printf("strongRef: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
hello = null;
System.out.printf("before gc: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
System.gc();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.printf("after gc: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
}
/**
* strongRef: reference=null, pollResult=Optional.empty
* before gc: reference=null, pollResult=Optional.empty
* [0.510s][info][gc] GC(1) Pause Full (System.gc()) 9M->4M(40M) 7.955ms
* after gc: reference=null, pollResult=Optional[java.lang.ref.PhantomReference@4450d156]
*/
@Test
public void phantomReference() throws InterruptedException {
MyObject hello = new MyObject("hello");
ReferenceQueue<MyObject> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
PhantomReference<MyObject> reference = new PhantomReference<>(hello, queue);
System.out.printf("strongRef: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
hello = null;
System.out.printf("before gc: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
System.gc();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.printf("after gc: reference=%s, pollResult=%s%n",
reference.get(), Optional.ofNullable(queue.poll()));
}